Androgenetic Alopecia

AGA: Androgenetic Alopecia
FAGA: Female Androgenetic Alopecia

▶Characteristics of AGA and FAGA
AGA (Androgenetic Alopecia) and FAGA (Female Androgenetic Alopecia) are types of hair loss conditions that cause progressive hair loss in specific areas of the scalp in men and women. In male pattern baldness, receding hairline and thinning on the crown of the head are the main features. In female pattern baldness, widening of the part line and decrease in hair volume are commonly observed. Generally, males tend to experience more advanced progression, which can lead to overall thinning of the hair.
▶Causes
The main cause is believed to be the conversion of the male hormone testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT) by the enzyme 5α-reductase, which then affects the hair follicles.
▶Mechanism
Hair follicles on the scalp are affected by DHT, leading to a shortened growth cycle and a shorter anagen (growth) phase. As the anagen phase gradually becomes shorter, the telogen (resting) phase is extended, resulting in thinning of the hair over time.
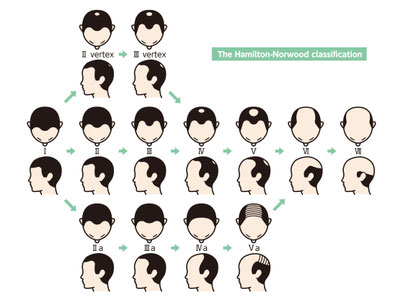
▶Progression Patterns of AGA
The most commonly used classification system for AGA is the "Hamilton-Norwood classification." It divides the symptoms of AGA into eight stages based on the areas of hair loss.
For example, Stage II indicates the early signs of AGA, such as a receding hairline. It is considered the initial stage of AGA.
As it progresses, it advances to Stage III, II-vertex, and III-vertex. At this point, it branches into the M-shaped pattern, where hair loss progresses from the frontal area, and the O-shaped pattern, where hair loss progresses from the vertex area.
Further progression leads to Stage IV-V, where it becomes challenging to distinguish between the M-shaped and O-shaped patterns. Finally, at Stage VII, the thinning of hair extends to the temporal regions.

▶Progression Patterns of FAGA
The classification commonly used for FAGA is the "Ludwig classification." It categorizes FAGA into three stages based on the areas of hair loss. As you can see, the progression pattern of hair loss in males and females differs significantly.
Type I: Thinning of hair and noticeable widening of the part line in the vertex area.
Type II: Generalized thinning of hair in the vertex area, with more visible scalp.
Type III: Further progression of hair loss in the vertex area, resulting in exposed scalp.
When FAGA develops, it disrupts the regular hair cycle, leading to the growth of thin and short hair strands. As a result, the characteristic feature of FAGA is overall thinning and miniaturization of hair, which reduces volume and exposes the scalp.
Treatment
▶Treatment Options
There are two main approaches to treating AGA:
①Treatment to inhibit the production of DHT (dihydrotestosterone) and prevent hair loss.
②Treatment to promote hair growth.
In the early stages of AGA, around stage II, treatment focused on preventing hair loss (option ①) may be sufficient. However, as AGA progresses, it is common to combine it with treatment to promote hair growth (option ②). Additionally, the medications used may vary slightly between males and females.
①Treatment to prevent hair loss
・Finasteride/Dutasteride (for AGA)
DHT is synthesized in the body from testosterone, a male hormone, through the action of an enzyme called 5α-reductase. They are medications originally used to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia (enlarged prostate), but they inhibit the action of this enzyme, thereby reducing DHT production and exhibiting an inhibitory effect on hair loss.
・Spironolactone (for FAGA)
This medication also has the potential to suppress DHT production. Originally used as a diuretic and anti-hypertensive drug for patients with heart failure, it inhibits the activity of aldosterone, a male hormone that raises blood pressure. It also inhibits the activity of androgens, male hormones with a structure similar to aldosterone. Since DHT is included in this group of androgens, it is believed to have a preventive effect on hair loss.
②Treatment to promote hair growth
・Minoxidil (for both males and females)
Minoxidil was initially developed as an antihypertensive drug for patients with high blood pressure. However, it was discovered that it had the side effect of promoting hair growth throughout the body. This led to its application in the treatment of hair loss, and it is now widely used for this purpose. Minoxidil is available as an oral medication and a topical solution applied directly to the affected areas. Generally, the oral medication is considered more effective. However, clinical trials conducted overseas have demonstrated hair growth effects with the topical solution as well. Combining the oral medication with the topical solution may enhance the overall effectiveness of the treatment.

▶Side Effects
・Finasteride/Dutasteride
These medications are contraindicated for use in women, especially breastfeeding and pregnant women. Because they are known to have adverse effects on the development of male reproductive function. They have the characteristic of "transdermal absorption," meaning that the active ingredients can be absorbed into the body simply coming into contact with the skin, even without ingesting the medication directly. The medication components can also be transferred to the semen. Therefore, if pregnancy is desired, it is recommended to discontinue the medication at least one month before attempting to conceive.
・Spironolactone
Since spironolactone is originally a diuretic, it may cause increased frequency of urination or lower blood pressure as potential side effects. It can also rarely cause menstrual irregularities or breast tenderness.
・Minoxidil
A characteristic side effect of minoxidil is "initial shedding." This refers to a temporary increase in hair loss shortly after starting the medication. However, many people may not even notice this effect. The increased hair loss will eventually subside, and hair regrowth will follow, so it is recommended to continue taking the medication for a while.
Additionally, other possible side effects of minoxidil may include palpitations, shortness of breath, edema, liver function impairment, telangiectasia (facial flushing), and hirsutism (excessive hair growth).
▶Prices
・The fees for these treatments include consultation fees and examination fees.
・Please note that the prices may be subject to change due to fluctuations in the cost of medications.
|
Dutasteride |
96,000Ks / 30tab |
|
Dutasteride + Minoxidil |
144,000Ks / 30tab each |
|
Spironolactone |
60,000Ks / 30tab |
| Spironolactone + Minoxidil | 120,000Ks / 30tab each |
|
Topical Minoxidil ※Optional |
36,000Ks / 30ml |
Please start by taking advantage of our free consultation.
Our physicians will assess the suitability of the treatment and answer any questions you may have.
To make a reservation, please click here.
* The prices on this page is as of July 2024
* The prices may change suddenly due to the currency or other economic situation in Myanmar
▶Medical Services
Consultation & Second Opinion
Medical Check-up
Vaccination
Rehabilitation
Weight-Loss Medications
Testosterone Therapy
Androgenetic Alopecia
Sexual Problems
▶Clinic Staffs
▶Contact
MYANMAR PREMIUM J MEDICAL CLINIC
No.3/A, Corner Of Bogyoke Aung San Road & 27th Street, Level 5, Junction City Tower Pabaedan Township, Yangon, Myanmar
Phone +95 9 8837 68885
E-mail mpjmclinic@gmail.com

